Cystitis- This is a pathology characterized by the development of the inflammatory process of the bladder wall due to the action of bacterial microorganisms.

Statistics of cystitis- One of the most common urological pathology. Women are more likely to experience this inflammation due to their morphological and physiological characteristics.
There are three ways for bacterial agents entering the bladder cavity:
- Ascending path- Through the urethra (urethra). The main role in this version of microbial penetration belongs to the anatomical and morphological characteristics of the female urinary tract: the short and wide urethra, closely related to the anus and vagina.
- Down path- From the kidney. This option develops as a process of kidney inflammation, such as chronic pyelonephritis.
- Hematoma path- The rarest option is certain when cystitis occurs immediately after an infectious disease, or when another source of suppurative infection is detected in a woman's body. Due to the anatomical anastomosis (connection) between the reproductive organs and the lymphatic vessels of the bladder, there is also the possibility of bacterial flora in the bladder.
The most common cause of bladder inflammation is E. coli (4 out of 5 cases, related to the anatomical and morphological characteristics mentioned above and the presence of this microorganism in the intestine).
Fewer cystitis is associated with Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and Enterococcus microorganisms. Gram vaginal rods can cause bladder inflammation due to instrumentation and surgical intervention.
Recently, the incidence of cystitis associated with fungal microorganisms is the simplest and viral incidence.
The introduction of infectious microorganisms is not enough to develop all inflammatory responses in the bladder, because the human body has a resistance mechanism for pathogenic bacterial effects.
Cystitis development factors
Therefore, in addition to etiologic factors, factors such as:
- Hemodynamic dysfunctionpelvic organs (blood circulation), especially the bladder;
- Disorders in bladder excretion function(urinary stagnation);
- Suppress all kinds of immune connections in the body(Vitamin deficiency, exposure to low temperatures, stress, fatigue, etc. );
- The enthusiasm of biochemical agentsand exchange products released in urine to the structure of the bladder wall;
- exposure to radiation rays;
- Not qualified with hygieneExternal genitals and random intercourse;
- Pathology of the gastrointestinal tractIn the presence, the bacteria accumulate and increase its activity, which then enters the urinary tract;
- Regular transfer of hormone metabolismThis leads to a lack of urethral tone and creates the best conditions for infection.
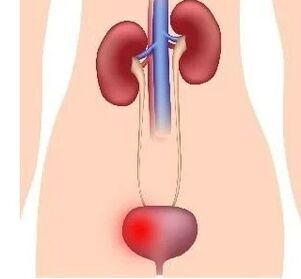
The first symptoms of cystitis in women
Clinics with acute cystitis in women are characterized by sudden onset and obvious complex symptomsand:
- The occurrence of frequent urination (Pollakiuria)It is characterized by frequency and small amount of urine released at least every 60 minutes. As frequent impulses develop, patients cannot control and maintain urine.
- Urination (violation of urination)Accompanied by pain in the substomy area (in the lower abdomen). As the degree of inflammation of the bladder wall progresses, these symptoms progress: the more development, the more impulses to urinate;
- Itching in the urinary tractAppears when urinating. Development occurs due to exposure to mucosa of urinary tract products metabolized by microorganisms that cause bladder inflammation.
- The appearance of bloodat the end of the Urine Act;
- The appearance of urine shadow, due to the absorption of a large number of blood cells (white blood cells and red blood cells), bacterial flora, cells on the surface of the inner wall of the bladder;
- There is no change in the characteristics of such patients.The patient's temperature index is characterized by normal or slightly increased (low enzyme) quantity. Scientists associate it with the fact that the mucosa of the bladder does not actually absorb the metabolites of microorganisms, which often lead to the development of symptoms characterized by poisoning and inflammation in the body.
The link between sudden symptoms and the link between women's body hypothermia. Acute inflammation can sometimes be observed for 2-3 days and disappear independently without treatment.

However, in most cases, the process takes more than 6 days, sometimes up to 15 days. In a subsequent date, the presence of the disease, in the case of treatment, requires the appointment of other examination methods to determine the body's concomitant pathology.
Pain signs of female cysts
In patients with acute cystitis, different severity of pain syndrome was observed:
- During mild inflammatory processes, the patient feels insignificant in the severity or pain of the lower abdomen.Sensitive pain at the end of Urination is accompanied by moderate pollakiuria. As the inflammation process develops further, the intensity of pain increases. The syndrome is then accompanied by the onset of urination or the entire behavior. Pain is not related to the behavior and is almost constant in nature, accompanied by a very painful palpation of the bladder projection.
- In the event of major cystitis, patients must urinate at least 2-3 times per hour, accompanied by obvious pain syndrome and the occurrence of urethral bleeding at the end of the bill. Pain can greatly worsen the quality of the patient's life because they don't go away all day.
The presence of blood cells and blood in urine (hematuria syndrome)
When an inflammatory process occurs on the bladder wall, it affects the fabric area at the ureteral confluence and near the urethra exit. The tissue becomes loose and bleeding.
This is manifested by the emergence of microorganisms and macroscopicity (or blood) in the urine, which is usually observed at the end of the urination method (terminal hematuria).
One of the most serious forms of acute cystitis is bleeding. This type of inflammation occurs when the red blood cells (red blood cells) in the blood that nourishes the arteries significantly penetrate into the bladder.
This option is available if the permeability of the blood vessel wall is increased (anemia, vitamin deficiency, disease of disease in blood system surgery) or damages bacterial cells (usually streptococcal flora) to the above wall. Urine falling into red blood cells in the urine stained by the foam cavity.
When hematuria occurs, the doctor is obliged to make a careful differential diagnosis between acute cystitis and a complex acute form of hemorrhagic cystitis. To this end, other examination methods were specified, the type of lesion was clarified, and the most correct treatment plan was selected.
Characteristics of acute and chronic cystitis in women
Sharp cystitis
Summarizing the above information, it is possible to distinguish between acute onset of the disease and specific symptom complexes of acute cystitis:
- Urinate a small amount,
- Pain syndrome of various properties,
- Itching associated with urination behavior,
- The blood drops at the end of the bill,
- The general condition of a woman remains unchanged.
Through real and timely diagnosis, the pathological condition is cured within 6-10 days. In the absence of improvement after 15 days of the disease process, it is worth considering the chronological period of inflammatory changes.

In addition to bleeding, there are two forms of complex acute cystitis:
- gangrene.Gangre forms are rarely found and occur due to impaired blood supply or bladder innervation. Clinically, this cystitis is manifested as dysfunction of urination, accompanied by pain, high body temperature, and pain in the S-bone area. This process is very dangerous to the occurrence of powerful complications such as peritonitis and requires rapid treatment measures.
- Blood floating.The form of floating blood is manifested through high body temperature, major poisoning of high body temperature, accompanied by the release of a small amount of urine (oligouria). Urine has such a complex current that it can obtain rotting odors, muddy features, thin flakes of fibrin formations, blood mixtures.
In the case of complex forms development, the duration of pathology increases significantly.
There is another form of cystitis - gap.It is characterized by inflammation of all urine bubble membranes. The clinic mainly urinates rapidly, reaching 180 times a day. After filling the bladder and urination methods, it reduces the active complaint of severe pain when it lowers the bladder and its return. The capacity of the bubbles is greatly reduced, so the above symptoms occur.
Chronic cystitis
Compared with acute, chronic cystitis is rarely used as a major pathology and is in most cases a secondary complication of the course of bladder, kidney, and urethral disease.
In view of this fact, it is necessary to carefully examine the body for the above pathological changes and to rule out or confirm the specific origin of the microorganism - the tuberculosis rod, invading the caterpillars.
Clinically, chronic cystitis is manifested by a continuous course, moderately different in the clinical analysis of complaints and urine, or in the form of recurrent pathology, with worsening (similar to the clinic of acute cystitis) and complete regression (with any manifestation of any pathological process).
Therefore, the objective manifestations of chronic cystitis correspond to the acute process. They are related to common protective properties in the human body, the cause of bacterial agents that cause the infection process, and the severity of inflammation. Pain, frequent urine, itching, the presence of blood and the shadow of urine are less obvious, and corresponds to the ongoing process and the recurrence of chronic cystitis.
Due to the inflammatory response of the mucosa, edema in all layers of the urinary wall and the increase in internal pressure create all conditions to form vesicles - all conditions for ritual reflux, i. e. casting the fluid cast from the bladder back to the ureter (connecting the kidney and foam).

Doctor - Urine scientists are engaged in the purpose of diagnosing and treating cystitis.
In order to correctly diagnose inflammatory pathology, it is necessary to clearly repair the patient's complaints and their medical history (before pathological development).
The clinical manifestations are very specific and can immediately indicate the presence of this disease, however, it is necessary to make a careful differential diagnosis between all types of cystitis and the bladder and other pathology of the disease.
Anatomically, data on the stress and effects of cryogenics, absorbed drugs, and other lesions in the pelvic organs and genital system will be useful.
After clarification of complaints and blood resection, clinical (general) urine analysis will be able to help validate the diagnosis - where increased levels of white and red blood cells will be detected (white blood cells and red blood cells).
To determine the type of bacterial microorganisms that cause the inflammatory process, urine seeding is a special nutrient medium that can be used in the future to select the most effective antibacterial drugs.
Before performing bacteriological examination, it is necessary to qualitatively treat areas of the external genitals by bactericidal solutions. Cystoscopy is contraindicated in the presence of acute inflammatory reactions.
To diagnose chronic cystitis, as well as collect complaints and data about the respiratory tract, cystoscopy is helpful during remission. This will determine all the necessary characteristics of the inflammatory disease. With this manipulation, biopsy material can be taken - soaked in the urine mucosa. In addition, to identify chronic cystitis, a sharp contrasting X-ray study is recommended.